Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
The absorption chiller model is a static “black box” model (see Figure6), in which experimental COP and chilling power are used to predict the chiller response at different boundary conditions. The chiller main parameters are: specific heat of oil (Cp0il), specific heat of chilled water (Cpch), auxiliary power for pumps and fans operation (Paux) and minimum refrigerant outlet temperature (Tset). The chiller inputs are: oil mass flow rate (moil), oil inlet temperature (Toili), ambient temperature (Tamb), chilled water mass flow rate (mch), chilled water inlet temperature (Tchi). The main outputs are oil outlet temperature (Toil, o) and the chilled water outlet temperature (Tch, o), from
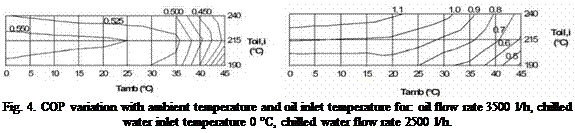 |
which driving heat rate (Q0ii), chilling power (Qch), rejected heat (Qamb) and chiller coefficient of performance (COP) are easily calculated. For a detailed description see [7].
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Nominal capacity |
13 kW |
|
Chilled water flow rate min / nom / max |
2300 l/h 2500 l/h 2900 l/h |
|
Initial charge of H2O |
11.5 kg |
|
Initial charge of NH3 |
8 kg |
|
Max. generator pressure |
35 bar |
|
Min. evaporator temperature |
-20 0C |
|
Table. 1. Main technical features of the Robur ACF 60 LB absorption chiller. |
Fig. 5. Chilling power (fraction of nominal value)
variation with ambient temperature and oil inlet
temperature for: oil flow rate 3500 l/h, chilled water
inlet temperature 0 °C, chilled water flow rate 2500l/h
![]()
![]() chiller
chiller
black box
model
Fig. 6. Absorption chiller black box model.
|
air
|
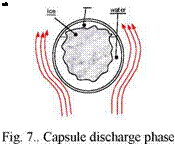 Fig8. Capsule charge phase
Fig8. Capsule charge phase