Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
In steady state conditions the useful heat of a solar thermal collector Quse, coll in W can be simply expressed by
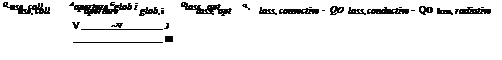 |
|
Optical losses [W]
![]() Incident solar radiation [W]
Incident solar radiation [W]
Solar radiation energy is incident on the collector at its aperture area Aaperture. This radiation Gglob, i consists of direct and diffuse radiation and is measured in the plane of the collector aperture. Two types of losses occur: optical losses and thermal losses. The terms used in eq. (1) are explained in detail in [5] and [6]. It depends on the construction of the collector and on its working temperature which kinds of losses are dominant and therefore have to be reduced.
In general, optical losses occur at the transparent cover of the absorber due to absorption and reflection as well as at the absorber by reflection. If reflectors are used, additional optical losses due to absorption and diffuse scattering of the reflected radiation have to be taken into account.
The optical losses include all incident solar radiation that does not reach the absorber of the collector. After absorption of the remaining part of radiation, convective losses occur due to natural convection in the gap between the absorber and its cover as well as due to forced convection by wind passing the cover. Conductive losses appear in the gap between the transparent cover and the absorber as well as through the back insulation or the frame of the collector. Both types of losses can be nearly eliminated by placing the absorber inside of a vacuum. Radiative losses of the absorber rapidly grow with increasing working temperature of a collector.
Radiative losses can be reduced by selective coating. Further reduction requires a relative small absorber area compared to the area of the aperture. Thus concentrators have to be applied to bundle the incident light on the absorber. In the SHIP Task different approaches
to reduce losses were considered and new types of collectors were developed.