Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
Thermal stagnation and risk for overheating is generally aimed to be avoided in any collector systems if these have metal-based — or polymeric collectors. The intention with a built-in overheating mechanism for polymeric collectors is to be able to use low-cost commodity plastics in glazed collectors.
High operational temperatures in polymeric collectors can be avoided by suitable hydraulic system design and dimensioning. Especially for solar combisystems with large collector areas the integration of the collectors into the facade reduces the risk for thermal stagnation during summer time.
At the same time it improves the performance during the heating season.
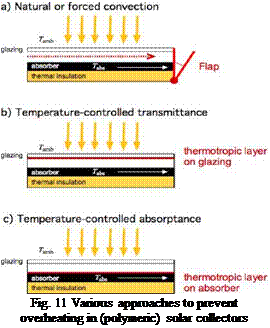
Natural or forced ventilation of the collector between absorber/glazing or absorber/thermal insulation can be used for the overheat protection of polymeric collectors. As illustrated in Fig. 11 (a) a flap is triggered by a temperature sensitive mechanism and opens when a critical temperature in the collector is reached, so that ambient air can ventilate and cool the collector [11, 12].
Functional materials / thermotropic coatings are a central topic in ‘Subtask C: Materials’ of IEA — SHC Task 39 and considerable R&D has been done, e. g. [13, 14, 15]: The principle is that the thermotropic coating switches from transparent to opaque at a critical temperature for the absorber material Tc. The coating can be applied on the glazing and reduces the transmittance (Fig. 11 (b)).or on the absorber and reduce the absorptance for temperatures above Tc (Fig. 11 (c)).
 |
Another principle for the overheat protection is proposed in the patent by Griessen and Slaman [16]. The refraction index of the collector glazing is changed by a simple mechanism and reduces the transmittance for solar radiation. The glazing is a prismatic structured optical layer, which is hollow inside. “The glazing is air-filled and transparent under normal operation but during stagnation filled with an appropriate fluid being totally reflective above the boiling point of the heat carrier in the absorber” [16].
Except for the first examples, the mechanisms for overheating protection are not commercial yet, but the R&D reveals the effort for making polymers with lower temperature resistance available for the use in glazed collectors.