Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
The high density of storage with chemical reactions makes the topic attractive. However many difficulties must be overcome to get to a commercial solution. The choice of an adequate reaction has kept attention at ECN, The Netherlands. A promising material is magnesium hydroxide seven hydrates which could theoretically store 777 kWh/m3 at 122 C.
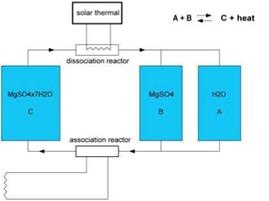 Fig. 13. Sketch of a future chemical heat store system with its three vessels, at ECN, the Netherlands (for a 12.2 MWh capacity, tanks volume could be: A 14 m3, B 5 m3, C 16 m3)/
Fig. 13. Sketch of a future chemical heat store system with its three vessels, at ECN, the Netherlands (for a 12.2 MWh capacity, tanks volume could be: A 14 m3, B 5 m3, C 16 m3)/
![]() This is a temperature that high performance solar collectors can achieve in summer time. The principle is to dry the material in summer with solar heat and in wintertime rehydratation can deliver back the energy (figure 13). Work with this material and its abitlity to de-hydrate and re-hydrate has just started.
This is a temperature that high performance solar collectors can achieve in summer time. The principle is to dry the material in summer with solar heat and in wintertime rehydratation can deliver back the energy (figure 13). Work with this material and its abitlity to de-hydrate and re-hydrate has just started.