Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
Fig. 2 represents the thermodynamic states of the ideal simple effect absorption cycle, assuming mechanical, thermal and chemical equilibrium and assuming energy degradation exclusively concentrated on expansion valves. Steady state mass and energy balance in components yield the following equations:
|
Evaporator (no superheating): |
|
|
Qm= m ref, K — h1); h1 = К |
(2) |
|
m ref, i X strong X weak Considering = |
(3) |
|
weak strong |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
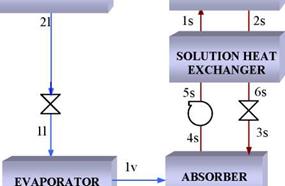
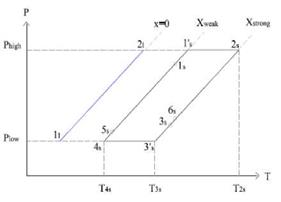

(a) (b)
Fig. 2. (a) LiBr/water absorption cycle. (b) Diagram P(T)-T LiBr/water
Generator (no superheating):
Mass balance:
|
Energy balance: Qoi = ™strong • h2s — mweak * К + ™^ ,г * h2v ; T2s = T2v |
![]()
™ weak = ™ strong + ™ ref, г
Solution heat exchanger:
![]() T — T T — T
T — T T — T
n = Js _4s = 2s 3s
hex, i
T1’s — T4s T2s — T 3’s

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
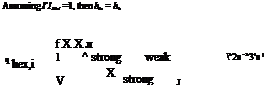 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|