Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
A single characterisation apparatus, described in figure 2, was designed and built to characterize the changing porous media. During synthesis reaction the salt reacts with steam and swells. The mass transfer through this porous media will be affected if the overall volume of the reactant remains constant. Moreover, the low working pressure (from 1000 to 10000 Pa) can lead to significant mass
transfer limitation if the permeability is very low. Therefore, to avoid mass transfer limitations, the working volume must grow as the reactive block swells. On the other hand, the overall kinetics, X, depends on heat and mass transfers. Thanks to this single apparatus, the overall kinetics, the swelling and the transfer coefficients will be linked together.
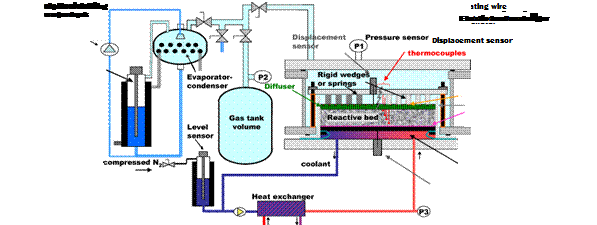
This experimental set up is described in figure 2. The disc located on the upper face of the reactive composite block, is a gas diffuser and a heat conductor as it includes a heating wire. On the lower face, there is a fluxmeter and a heat exchanger wall which can move. This very special device allows the reactive composite volume to swell during the reaction. The gas diffuser and the heat exchanger wall are connected to a displacement sensor. Several rigid wedges or springs are located between the gas diffuser and a fixed plate above it. Four thermocouples are in the reactive bed at different depth, and a pressure sensor measures the reactor pressure. The gaseous part of this reactor is connected to a gas tank and to an evaporator/condenser, whose pressure is measured by another pressure sensor. The evaporator/condenser is also connected to the liquid water tank, which includes a level sensor to measure the amount of reacting water.
Another liquid tank is used to control the location of the heat exchanger wall, under the lower face of the composite. The coolant fluid in this tank is connected on one side to this heat exchanger plate and on the other side to a compressed nitrogen bottle. The level of coolant in this tank gives information on the position of the exchanger plate. The coolant pressure is constant and it is given by a pressure sensor; the working volume of the reactant is not constant.