Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
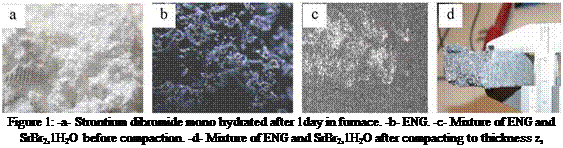 |
The reactive bed is made up of natural expanded graphite and strontium dibromide mono or hexahydrated, SrBr2(1-6)H2O, see figure 1. The ENG particles have a worm shape and their density is about 4 kg. m-3. The salt is a powder with particle size about 100 pm. Its density is close to 890 kg. m-3. These two compounds were mixed together to obtain a composite block of apparent density of ENG p and of mass ratio of ENG, wl. After mixing, the composite is compacted to reach the thickness zs, Table 1.
To make easier comparison between composite blocks, the energy density, Dec, was defined as in equation 1. nG is the number of moles exchanged during reaction, Arh° is the molar enthalpy of the reaction between salt and steam and Vr is the apparent volume of the composite block.
The transfers in the reactive block are characterized by the permeability k, the Klinkenberg’s coefficient b and the effective thermal conductivity X. In the above mentioned bed the open porosity s connects the steam produced by the evaporator and the reactive salt.