Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
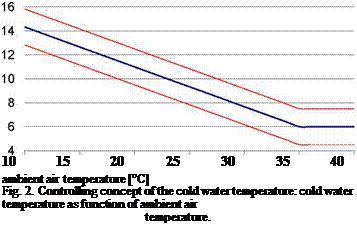
The cold water temperature of the cold water supply network is driven as function of the ambient air temperature as shown with the diagram in Figure 2.
cold water
temperature [°C]
The cold water temperature can be differing from the target temperature in the range of ±1.5 K, which is depicted in the diagram by the red lines (upper and lower lines). If the temperature of the cold water return flow (means the cold water back flow from the cold consumer) drops under the target cold water temperature more than 1.5 K, the chiller is switched off. This leads to a timing operating of the absorption chiller especially in part load.
Furthermore, the operation mode of free cooling is realised. If the wet bulk temperature drops under the cold water temperature with more than 8 K, the operating mode of the solar cooling plant changes into free cooling. This means, that the cold capacity of the plant is not generated by the absorption chiller anymore, but directly by the cooling tower via an additional heat exchanger connecting the cold water cycle with the re-cooling water cycle. Because this operating mode often occurs in spring and autumn, the heat generated by the solar collector field at this moment can be provided as surplus heat to the heating system of the institute via the heat exchanger WT 2.
In the case of low solar irradiation but cold demand, the absorption chiller can also be driven by heat from the heating system of the institute. The heating system of the institute consists of a gas fired boilers and a micro-gas turbine. Especially in summer time, when there is no space heating demand, exclusively the micro-gas turbine is used to provide the necessary heat for the absorption chiller. At this moment, the system is operating as combined heat, cold and power generation plant.
2. Operational experiences