Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
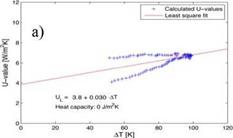
The heat loss coefficient UL is determined according to Section 2.3 for the measurements with the reference collector (not ventilated) and a collector tilt angle of 45° (data of June 10, 2006). The slope U2 and the interception with the y-axis U are found by linear regression, see Fig. 6 (a, b). In the case of (a) and (b) we find: UL= 3.8 + 0.030 AT (red line).
 |
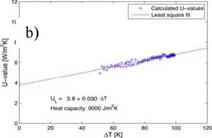 |
The collector’s heat capacity is not accounted for in (a), hence the derived UL-values of the measurements in the morning and afternoon do not coincide. By choosing the heat capacity Ce=9 kJ/(m2 K) in (b) the AT-dependent heat loss coefficient from the morning and afternoon match. The chosen heat capacity Ce does not have a significant influence on the UL-values as long as the measurements before and after noon cover about the same AT interval. The U-values were determined for different tilt angles and the resulting collector efficiencies have been compared with earlier efficiency tests of the same collector. The presentation and discussion of these results would exceed the frame of the present work; it is referred to [19].
Fig. 6. U-value UL as a function of the temperature difference AT between the mean absorber temperature
and the ambient temperature if the collector’s heat capacity Ce is set to zero (a) and to 9 kJ/(m2 K). The line
represents the least square fit; results based on raw data of measurements performed at set-up A.