Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
The equations developed for each configuration are very similar. Therefore, they are presented here only for configuration C. The thermal network associated with this configuration is shown in Fig.
2.
![]()
![]()
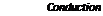
 ] Convection
] Convection
The energy balance equations performed in the middle of the outer glazing layer (go), outer air cavity (ao), PV laminate outer glass layer (Lo), PV+EVA layer (Lm), PV laminate inner glass layer (Li), inner air cavity (oi) and inner glazing layer (gi) are written as follows:
4 4 dT
![]()
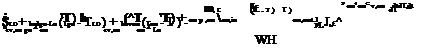 |
|
Sgo — hcv, cmb To — Tamb ) — ™go, o (Tgo — Tsur ) — hcv, ao (Tgo — Too ) — hrd, go-Lo (Tgo — TLo ) = PgotgoCv, go
![]()
![]() S — p, (TLo — TLm) (TLm ~ TLj) _p f C ^T^
S — p, (TLo — TLm) (TLm ~ TLj) _p f C ^T^
Lm PV r r Lm Lm v, Lm dt
Rcd, Lo-Lm Rcd, Lm-Li d
(T — T ) dT
TLm — Li — hrd, Li — ATLi — Tgi) — hcv, ai(TLi — Tai) _ pjtT^—Lr
Rcd rm-n dt
In Equations (1) to (7), Sj represents the amount of solar radiation absorbed by layer j, ejo and j are the outdoor and indoor surface emissivity for layer j, Tamb and Tin are the ambient and indoor environment temperatures, Tj is the temperature of layer j, a is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, Cp, ao is the specific heat at constant pressure of the air in the outer air cavity, W and H are the window width and height, Rcdj-k and hrdJ_k are the conductive thermal resistance and radiative heat transfer coefficient between layers j and k, and pj, tj and CvJ- represent the density, thickness and specific heat at constant volume of the material of layer j, respectively. hcv, in is the indoor heat transfer coefficient calculated with the relation of Curcija and Goss [6], while hcv, amb represents the outdoor heat transfer coefficient obtained with the correlation of Cole and Sturrock [7]. The outer and inner air cavities convective heat transfer coefficients, hcv, ao and hcvai,,are estimated with the relations developed by Wright [8] for non-ventilated vertical air cavities. For the naturally vented cavity, the outer and inner convective heat transfer coefficients, mass flow rate (mao) and air inlet (Taoin) and
outlet temperatures (Taoout) are determined with the correlations found in ASHRAE [9]. The surroundings temperature, Tsur, is a function of the sky temperature, Tsky, and the ground temperature, Tgnd, and is given as
Tur =F( + FgndTAgnd ) (8)
In Equation (8), Fsky and Fgnd are the view factors between the window and the sky, and the window and the ground, respectively, and correspond to 0.5 for vertical surfaces. PPV in Equation
(4) is the power produced by the PV cells at maximum power point per laminate unit area and is calculated as a function of irradiance and cells temperature with the relation found in Poissant et al. [10]. The cells were assumed to be crystalline silicon and the rated peak power of the PV assembly in the 1.44m2 laminate was set to 165W. The total irradiance striking the PV cells and the solar radiation absorbed in each layer were determined by ray-tracing technique by taking into account incidence angle effects and multiple reflections.