Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
The simplest mode for concentrating photovoltaics is the combination of plain PV modules with flat diffuse reflectors. The increase of the energy output of PV modules can be achieved by using flat diffuse reflectors as boosters to the PV modules, which give an almost uniform distribution of the reflected solar radiation on PV surface. In horizontal roof installations (Fig. 1-i), the PV modules are usually placed in parallel rows, with a distance between them to avoid shading. A fraction of the incoming solar radiation on the horizontal PV installation is not used by PV modules from Spring to Autumn, as solar rays are striking the free horizontal surface between the parallel PV rows. This fraction of radiation could be partially used by the PV modules if booster
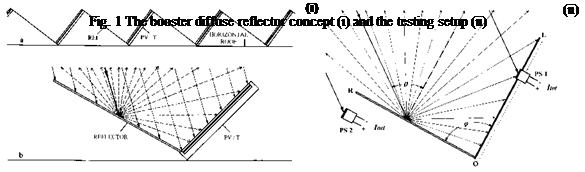 |
diffuse reflectors are placed between the parallel PV rows and increase the solar radiation on PV surface. The diffuse booster reflectors achieve a smoother distribution of the additional solar radiation on PV surface, which is almost uniform for some reflector-PV module geometries [20]. The additional solar input on the surface of PV modules is lower than that of specular reflectors, but diffuse reflectors are cheaper and can be combined easily with typical size PV modules.
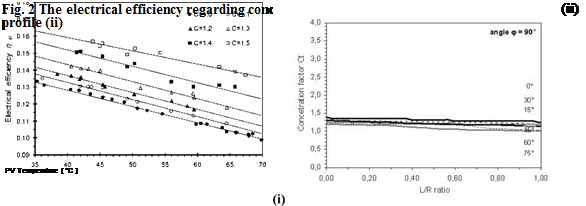 |
Photovoltaic modules of pc-Si type with aluminum diffuse reflector were tested with variable percentage of the additional solar radiation from the diffuse reflector, with respect to its electrical efficiency as a function of the PV module temperature. The efficiency Пеі was calculated for C=1 to C=1.5 (with step 0.1), adjusting properly the device for the achievement of the corresponding values of total solar radiation on PV module surface during noon. To keep stable the PV temperature TPV during the experiments, water was circulated through a heat exchanger of a thermal unit mounted on PV rear surface. In Fig. 2-i the results from these tests are presented.
To measure the effective concentration factor Ct of the diffuse reflector, angles ф of 90° and 120° between the reflector and the plane of the PV module were selected and the distribution of solar radiation on the PV surface as function of the angle of incidence в was derived. The angle ф=90° gives satisfactory results, while ф=120° is an upper limit of effective angles. A photosensor of small c-Si PV cell (1 cm2) was used to measure the net Inet and the total Itot incident solar radiation on the plane of PV module. In Fig. 1-ii the device for the measurement of the concentration factor Ct for variable values of the ratio L/R is shown. L is the PV module width [OL] and R the reflector width [OR] respectively. In practical applications L/R<1 should be considered. In the experiments a flat aluminium sheet with satisfactory diffuse reflection profile was used (Fig. 2-ii).