Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
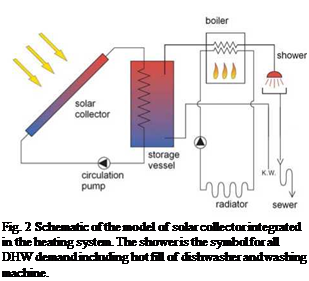
The solar collector and the storage vessel were modelled in Matlab. A collector heats the water in the primary loop, shown on the left in figure 2, allowing a temperature stratification within the storage vessel. Water at the top of the vessel is extracted for space heating, DHW and hot fill and simultaneously cold water (10°C) is fed to the bottom of the vessel. If the temperature of the extracted water is too low, the boiler will heat it to the desired level: 40 °C for space heating, 55°C for DHW and 60°C for hot fill. The latter values are relatively high in order to prevent Legionella contamination. The water at 55°C is mixed with cold water to obtain the desired temperature level of the DHW tapings.
The type of collector is a vacuum collector[5] of varying size, oriented towards the south with a tilt of 45 degrees. The storage vessel is modelled as a cylindrical vessel of varying size which is thermally insulated with a U-value of 0.1-0.2 W/m2K. The temperature stratification in the vessel is modelled as 8 isothermal segments of water.
 |
In the base case scenario, the DHW pattern is modelled after that in the Dutch Energy Performance Norm EPN [6], which entails approx. 20 short and longer tapings of a particular temperature level including a long taping of 50 l every morning and every evening for showering. The pattern for the hot fill of dishwasher is a daily taping of 14 l at 60°C and that for the washing machine two tapings of 13 l on Saturday and Sunday each and another on Monday. This pattern and a number of variants (see chapter 3.2.5) were simulated and the contribution to the saving of primary energy was calculated.