Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
1.1. Experiment facility
Roof testing materials in four measurement boxes (inside measurement 300^300) were set up in the upper part of the center of the experiment facility shown in Fig.2. A pair of roof testing materials W (perspirable roof material + light structural roof) and a pair of roof testing materials D (light structural roof only) were made. The temperature and the heat flow rate were measured and compared by the
![]()
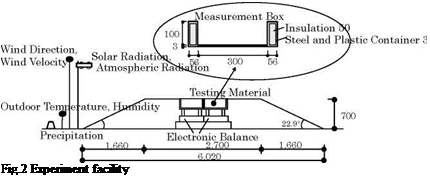 |
couple (D and W), and the rate of evaporation was measured from the weight change of the measurement box of the other couple. Fig.3 shows measurement point of the temperature and the heat flow rate. The experiments were performed in Tsu City, Mie Prefecture, Japan in summer of 2006. The specific sense temperature of the hydrogel was set at 25-30 °С, by taking the actual outdoor condition in summer into account. The water absorption magnification was set to be about 150 times of the weight of the hydrogel, by supplying water in the night time, once a day.
Fig.4 shows the example of the experimental results of each measurement box. By comparing measurement results of the boxes D and W, the decrease rate of the temperature and the heat flux (heat gain) due to the evaporative cooling of perspiration are as follows, (as each maximum value during the experiment period for the sample (1)), the roof surface temperature (D2-W2) is about 32 °С, surface temperature under the box (D4-W4) is about 4 °С, heat flow rate of steel plate outer surface (DF1- WF1) is about 107W/m2, surface heat flow under the box (DF2-WF2) is about 13W/ m2, and for the sample (2), the roof surface temperature (D2-W2) is about 33 °С, surface temperature under the box (D4-W4) is about 4 °С, heat flow rate of steel plate outer surface (DF1-WF1) is about 137W/ m2, surface heat flow under the box (DF2-WF2) is about 13W/ m2. The maximum evaporation rate is 1.02kg/(m2-h) in the sample (1) and 1.08kg/(m2-h) in the sample (2). The thermal effectiveness due to the evaporative cooling is large in each sample of the perspirable roof. For each sample, evaporation occurs in conformity with the relationship between the surface temperature of the sample and the specific sense temperature of the hydrogel.
The analysis method adopted is of calculating multi-room temperature, heat load and ventilation rate with the use of simultaneous non linear equations of room heat balance, room air rate balance, wall outer and inner surface heat balances, with room temperature, room pressure, wall outer and inner surface temperatures for each room set as unknown quantities, as shown in literature[4,5]. As for the heat conduction calculation of the wall, the finite difference method (implicit scheme) is used. Fig.5
shows the calculation flow of the autonomous perspiration on the wall surface. The calculation time interval is assumed to be 1hr in this calculation.