Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
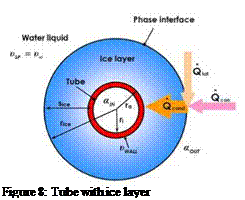
Figure 5 shows a tube covered with an ice layer. The media temperature in the tube is lower than the temperature in the ice layer and the surrounding liquid phase. Basically solidification Processes can be described mathematically with the following equations assuming quasi-stationary conditions [3].
|
= X * A * cond ice ice |
|
Qlt = Ah * m = p. * Ah lat s ice ice s |
|
Figure 8: Tube with ice layer |
|
Q cond Q lat + Q con The conducted heat flow rate is calculated |
|
33 dr |
|
ice |
|
dVic |
|
dt |
|
(1) (2) (3) |
|
ice |
|
The equation for the latent heat fraction is |
|
r |
|
Q |
The heat balance at the ice layer surface was calculated with equation (1)
The convective heat fraction was calculated with equation (4)
|
(4) |
![]() Qcon =aout * Aice *(^-^s )
Qcon =aout * Aice *(^-^s )
The rate of increase in the volume of solid ice is calculated from
d V. dr
ice _ 2* r * n *L * lce
dt dt
Substituting Equation (2), (3), (4) and (5) in Equation (1) yields
|
t *9* tt^-T * ice, sol ‘ Tube ice |
|
aout *2*n* LTube * rice *(Soo — Ss ) +Pice * Ahs *2*n* L |
|
dric |
|
ice |
|
Tube ice |
|
dt |
|
dS |
|
r ice |
|
(6) |
|
|
SHAPE * MERGEFORMAT
