Как выбрать гостиницу для кошек
14 декабря, 2021
Two different cubicles were built:
1. Reference cubicle: The alveolar brick has an especial design which provides both thermal and acoustic insulation. No additional insulation was used in this cubicle.
2. PCM cubicle: Several CSM panels (Fig. 3) containing SP-25 A8 hydrate salt are located inside the cubicle, between the alveolar brick and the plaster plastering in order to increase the thermal inertia of the wall (in the southern and western walls and the roof).
|
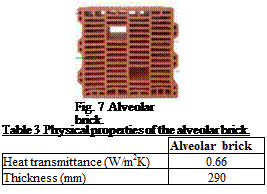
Fig. 7 Alveolar brick. |
|
Table 3 Physical properties of the alveolar brick.
|
|
Table 4 Physical properties of SP-25 A8.
|
 |
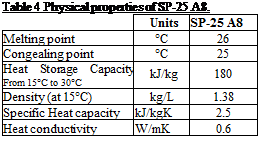 |
Fig. 7 presents the alveolar brick. The most important properties of the alveolar brick and SP-25 A8 are shown in Table 3 and Table 4.
|
Fig. 8 Demonstration cubicles built with alveolar brick. |

Fig. 8 shows the demonstration cubicles built with alveolar brick.
1.1. Instrumentation and registered data
To evaluate the insulating performance of each material the following data were registered for each cubicle.
• Wall temperature (east, west, north, south internal, south external, roof and floor).
• Internal ambient temperature (1.5 m) and humidity.
• Heat flux at the south wall (inlet and outlet).
• Electrical consumption of the heat pump.
• Solar radiation.
• External ambient temperature and humidity.
1.2. Experiments performed
The experimental set-up offers the possibility to perform two kinds of tests.
• Free-floating temperature, where no heating/cooling system is used. The temperature conditions in the cubicles are compared. The ones with PCM are expected to present a better behavior.
• Controlled temperature, where a heat pump is used to set the ambient temperature of the cubicle. The energy consumption of the cubicles is compared using different set points. The cubicles using PCM are expected to present lower consumptions.